
题目描述
San Bytecisco is a beautifully situated coastal town. It consists of  small, yet densely populated islands, numbered from
small, yet densely populated islands, numbered from 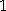 to
to  . Certain islands are connected with bridges, used for (bidirectional) road traffic. Each pair of islands can be connected with at most one bridge. The islands are connected in such a way that every island can be reached from every other by using the bridges only.
. Certain islands are connected with bridges, used for (bidirectional) road traffic. Each pair of islands can be connected with at most one bridge. The islands are connected in such a way that every island can be reached from every other by using the bridges only.
Byteasar and Bytie are going for a bike trip in San Bytecisco. The will start their ride at the island no. 1. They intend to visit every island, while passing along every bridge once and ending the trip where it began, i.e., the island no. 1. Being quite seasoned riders, they expect some serious trouble from… the wind! After all, it is very windy along the coast, and especially so on the bridges between the islands. Obviously, depending on its speed and direction, the wind makes it hard to cross the bridge in different extent for either direction. For simplicity we will assume for every bridge and direction of crossing, the opposing wind speed is constant.
Help Byteasar and Bytie to find a route as they desire that will in addition be the least tiresome. Byteasar and Bytie agreed on the maximum opposing wind speed as a measure of a route’s tiresomeness.
Input
In the first line of the standard input there are two integers separated by a single space:  and
and 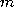 (
(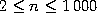 ,
, 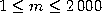 ), denoting the number of islands and the number of bridges in San Bytecisco respectively. The islands are numbered from 1 to
), denoting the number of islands and the number of bridges in San Bytecisco respectively. The islands are numbered from 1 to  , while the bridges from 1 to
, while the bridges from 1 to 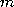 . The following
. The following 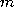 lines specify the bridges. The line no.
lines specify the bridges. The line no. 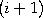 contains four integers
contains four integers 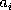 ,
, 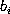 ,
, 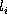 ,
, 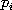 (
(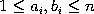 ,
, 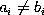 ,
, 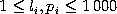 ), separated by single spaces. These denote that the bridge no.
), separated by single spaces. These denote that the bridge no. 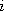 connects the islands no.
connects the islands no. 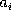 and
and 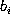 . The opposing wind speeds are
. The opposing wind speeds are 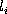 when one goes moves from
when one goes moves from 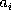 to
to 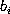 , and
, and 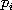 if one goes from
if one goes from 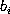 to
to 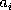 .
.
Output
If there is no route satisfying the requirements of the daring two riders, the first and only line of the standard output should hold the word NIE (no in Polish). Otherwise, the output should have two lines, specifying the least tiresome route over San Bytecisco. The first line should hold the maximum opposing wind speed for that route, i.e., the number we wish to minimize. The second line should hold 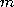 integers, separated by single spaces, giving the numbers of successive bridges one crosses on the least tiresome route.
integers, separated by single spaces, giving the numbers of successive bridges one crosses on the least tiresome route.
Should there be more than one least tiresome route, your program can pick one arbitrarily.
题解:
这道题裸的混合图求欧拉回路,直接搞就完了,输出方案的时候倒着输出即可。
代码:
|
|




近期评论