
QuickStart For Numpy
1 2 3 4
|
import numpy as np a = np.arange(15).reshape(3,5) a
|
array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14]])
(3, 5)
2
dtype('int64')
15
numpy.ndarray
1 2 3
|
b = np.array([6, 7, 8]) b
|
array([6, 7, 8])
2. Array Creation
2.1 create array by regular Python list or tuple
1 2 3 4
|
import numpy as np a = np.array((2, 3, 4)) a
|
array([2, 3, 4])
1 2
|
b = np.array([5, 6, 7]) b
|
array([5, 6, 7])
1 2
|
c = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]) c
|
array([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]])
2.2 create array by functions
1 2 3
|
a = np.zeros((3,4)) a.dtype
|
dtype('float64')
1 2 3
|
b = np.ones((2, 3), dtype = np.int16) b
|
array([[1, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1]], dtype=int16)
1 2 3 4
|
c = np.empty((2, 2)) c
|
array([[ 6.94428861e-310, 1.15911595e-316],
[ 4.76862566e+180, 1.63041663e-322]])
array([10, 15, 20, 25])
array([ 0. , 0.25, 0.5 , 0.75, 1. , 1.25, 1.5 , 1.75, 2. ])
3. printing Arrays
1 2 3 4
|
a = np.arange(6) print(a)
|
[0 1 2 3 4 5]
1 2 3 4
|
b = np.arange(12).reshape(4,3) print(b)
|
[[ 0 1 2]
[ 3 4 5]
[ 6 7 8]
[ 9 10 11]]
1 2 3
|
print(np.arange(10000))
|
[ 0 1 2 ..., 9997 9998 9999]
1
|
print(np.arange(10000).reshape(100, 100))
|
[[ 0 1 2 ..., 97 98 99]
[ 100 101 102 ..., 197 198 199]
[ 200 201 202 ..., 297 298 299]
...,
[9700 9701 9702 ..., 9797 9798 9799]
[9800 9801 9802 ..., 9897 9898 9899]
[9900 9901 9902 ..., 9997 9998 9999]]
4. Basic Operations
4.1 Arithmetic operations on arrays apply elementwise
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
|
a = np.arange(4, dtype = np.float64) b = np.array([2, 3, 4, 5]) print(a+b) print(a-b) print(a*b) print(a/b)
|
[ 2. 4. 6. 8.]
[-2. -2. -2. -2.]
[ 0. 3. 8. 15.]
[ 0. 0.33333333 0.5 0.6 ]
1 2 3 4
|
print(b**2) print(np.sin(a)) print(a<3)
|
[ 4 9 16 25]
[ 0. 0.84147098 0.90929743 0.14112001]
[ True True True False]
4.2 matrix product
1 2 3 4 5 6
|
A = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]]) B = np.array([[4, 2], [3, 1]]) print(A*B) print(A.dot(B))
|
[[4 4]
[9 4]]
[[10 4]
[24 10]]
4.3 unary operations
1 2 3 4 5
|
a = np.arange(1, 5) print(a) print(a.sum()) print(a.max()) print(a.min())
|
[1 2 3 4]
10
4
1
1 2 3 4 5 6
|
b = np.arange(1, 5).reshape(2, 2) print(b) print(b.sum()) print(b.sum(axis = 0))
|
[[1 2]
[3 4]]
10
[4 6]
5. Universal Functions
1 2 3
|
B = np.arange(3) print(np.exp(B)) print(np.sqrt(B))
|
[ 1. 2.71828183 7.3890561 ]
[ 0. 1. 1.41421356]
See also:
all, any, apply_along_axis, argmax, argmin, argsort, average, bincount, ceil, clip, conj, corrcoef, cov, cross, cumprod, cumsum, diff, dot, floor, inner, inv, lexsort, max, maximum, mean, median, min, minimum, nonzero, outer, prod, re, round, sort, std, sum, trace, transpose, var, vdot, vectorize, where
6. Indexing, Slicing and Iterating
array([ 0, 1, 8, 27, 64, 125, 216, 343, 512, 729])
1 2
|
print(a[2]) print(a[2:5])
|
8
[ 8 27 64]
1 2 3
|
a[:6:2] = -1000 print(a) print(a[::-1])
|
[-1000 1 -1000 27 -1000 125 216 343 512 729]
[ 729 512 343 216 125 -1000 27 -1000 1 -1000]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
|
def (x, y): return 10*x+y b = np.fromfunction(f, (5, 4), dtype = int) print(b)
|
[[ 0 1 2 3]
[10 11 12 13]
[20 21 22 23]
[30 31 32 33]
[40 41 42 43]]
1 2 3 4
|
print(b[2,3]) print(b[0:5,1]) print(b[:,1]) print(b[-1])
|
23
[ 1 11 21 31 41]
[ 1 11 21 31 41]
[40 41 42 43]
1 2 3 4 5 6
|
A = np.array([[1,2],[3,4]]) print(A) print(A.flatten()) for element in A.flat: print(element)
|
[[1 2]
[3 4]]
[1 2 3 4]
1
2
3
4
7. Shape Manipulation
7.1 Changing the shape of an array
1 2 3 4
|
a = np.floor(10*np.random.random((3,4))) a
|
array([[ 7., 1., 9., 6.],
[ 9., 1., 5., 9.],
[ 9., 7., 9., 1.]])
(3, 4)
[ 7. 1. 9. 6. 9. 1. 5. 9. 9. 7. 9. 1.]
[[ 7. 1.]
[ 9. 6.]
[ 9. 1.]
[ 5. 9.]
[ 9. 7.]
[ 9. 1.]]
[[ 7. 9. 9.]
[ 1. 1. 7.]
[ 9. 5. 9.]
[ 6. 9. 1.]]
1 2 3 4 5
|
print(a) print(a.resize(2,6)) print(a)
|
[[ 7. 1. 9. 6.]
[ 9. 1. 5. 9.]
[ 9. 7. 9. 1.]]
None
[[ 7. 1. 9. 6. 9. 1.]
[ 5. 9. 9. 7. 9. 1.]]
7.2 Stacking together different arrays
vstack() and hstack()
1 2 3 4 5 6
|
a = np.arange(1,5).reshape(2,2) b = np.arange(5,9).reshape(2,2) print(a) print(b) print(np.vstack((a,b))) print(np.hstack((a,b)))
|
[[1 2]
[3 4]]
[[5 6]
[7 8]]
[[1 2]
[3 4]
[5 6]
[7 8]]
[[1 2 5 6]
[3 4 7 8]]
array([1, 2, 3, 0, 4])
array([[1, 3, 5, 7]])
7.3 Splitting one array into several smaller ones
1 2
|
a = np.arange(1,25).reshape(2,12) print(a)
|
[[ 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12]
[13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24]]
[array([[ 1, 2, 3, 4],
[13, 14, 15, 16]]), array([[ 5, 6, 7, 8],
[17, 18, 19, 20]]), array([[ 9, 10, 11, 12],
[21, 22, 23, 24]])]
1 2 3
|
print(np.hsplit(a,(3,4)))
|
[array([[ 1, 2, 3],
[13, 14, 15]]), array([[ 4],
[16]]), array([[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12],
[17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24]])]
8. Copies and Views
8.1 No Copy at All
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
|
a = np.arange(12) b = a print(b is a) b.shape = 3,4 print(a.shape)
|
True
(3, 4)
8.2 View or Shallow Copy
1 2 3 4 5 6
|
c = a.view() print(c is a) print(c.base is a) print(c.flags.owndata)
|
False
True
False
1 2 3 4
|
c.shape = 2,6 print(a.shape)
|
(3, 4)
1 2 3 4 5
|
print(c) c[0,4] = 1234 print(c) print(a)
|
[[ 0 1 2 3 4 5]
[ 6 7 8 9 10 11]]
[[ 0 1 2 3 1234 5]
[ 6 7 8 9 10 11]]
[[ 0 1 2 3]
[1234 5 6 7]
[ 8 9 10 11]]
1 2 3 4 5
|
s = a[:,1:3] s[:] = 10 print(a)
|
[[ 0 10 10 3]
[1234 10 10 7]
[ 8 10 10 11]]
8.3 Deep Copy
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
|
d = a.copy() print(d is a) print(d.base is a) d[0,0] = 9999 print(a)
|
False
False
[[ 0 10 10 3]
[1234 10 10 7]
[ 8 10 10 11]]
9. Indexing with Boolean Arrays
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24
|
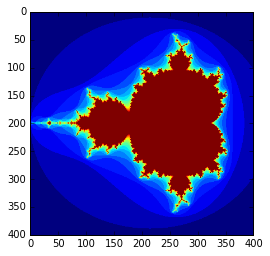
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt def mandelbrot(h, w, maxit=20): """ return an image of the Mandelbrot fractal of size (h, w)""" y,x = np.ogrid[-1.4:1.4:h*1j, -2:0.8:w*1j] c = x + y * 1j z = c divtime = maxit + np.zeros(z.shape, dtype = int) for i in range(maxit): z = z**2 + c diverge = z*np.conj(z) > 2**2 div_now = diverge & (divtime == maxit) divtime[div_now] = i z[diverge] = 2 return divtime plt.imshow(mandelbrot(400,400)) plt.show()
|






近期评论