
Implementations
Selection Sort
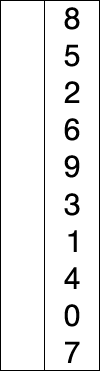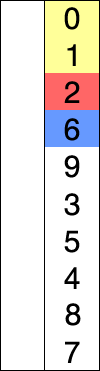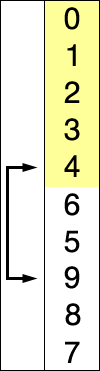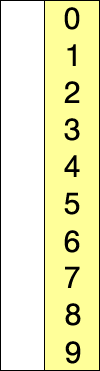
generally performs worse than the similar insertion sort.
The algorithm divides the input list into two parts: the sublist of items already sorted, which is built up from left to right at the front (left) of the list, and the sublist of items remaining to be sorted that occupy the rest of the list. Initially, the sorted sublist is empty and the unsorted sublist is the entire input list. The algorithm proceeds by finding the smallest (or largest, depending on sorting order) element in the unsorted sublist, exchanging (swapping) it with the leftmost unsorted element (putting it in sorted order), and moving the sublist boundaries one element to the right.
1 |
public int[] selectionSort(int[] array) { |
Insertion Sort

Insertion sort iterates, consuming one input element each repetition, and growing a sorted output list. At each iteration, insertion sort removes one element from the input data, finds the location it belongs within the sorted list, and inserts it there. It repeats until no input elements remain.
- Efficient for (quite) small data sets, much like other quadratic sorting algorithms
- More efficient in practice than most other simple quadratic algorithms such as selection sort or bubble sort
- efficient for data sets that are already substantially sorted, the time complexity is O(nk) when each element in the input is no more than k places away from its sorted position
- stable
Array based
1 |
public int[] insertionSort(int[] array) { |
LinkedList based
1 |
public ListNode (ListNode head) { |
Bubble Sort

insertion sort, generally run faster than bubble sort.
1 |
public static int[] bubbleSort(int[] array) { |
Merge Sort





近期评论